Home >> Shape & Space - Triangle Similarity
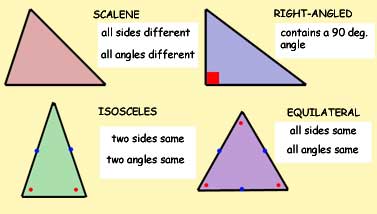
Triangle types
Definition of similarity
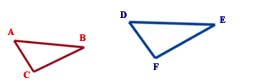
A triangle (or indeed any two dimensional shape) is deemed similar to another if it has the same shape but a different size.
Similarity and Proportion - If triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF then:
![]()
Triangle enlargement - in the above example, the ratio of the sides(largest over smallest) gives the Scale Factor.
For enlargement the Scale Factor is greater than one( >1 ).
The Centre of Enlargement is a point used for constructing an enlargement from an original shape.
The Scale Factor is used to calculate where the new points on the enlarged shape are from the centre of enlargement.
Example - A right angled triangle positioned as shown, 2cm from a point P. Using the point P as reference, enlarge the triangle by a factor of 2.
The solution is to measure the distance between each of the points of the triangle to the point P, and then to multiply each distance by the scale factor 2.
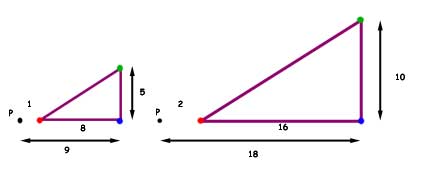
Triangle reduction - here the Scale Factor is less than one( <1 ).
The ratio is of the small sides of the first triangle to the large sides of the second triangle.
![]()
Negative enlargement/reduction - here the shape is either enlarged or reduced as before but is rotated through 180 degrees.
[ About ] [ FAQ ] [ Links ] [ Terms & Conditions ] [ Privacy ] [ Site Map ] [ Contact ]
